What is friction spinning?
· The friction
spinning is a type of open-end spinning method of yarn spinning process. The
yarn formation in the friction spinning takes place in the yarn forming zone
consisting of two friction rollers with the help of frictional forces.
· First of
all, the fibres are converted into a strand of fibres and the fibres strand is
kept almost equal to the final count of the yarn. Now, the twist is inserted to
form the yarn.
· In the
case of open end friction spinning, the fibre supply is opened completely into
individual fibres. These fully opened fibres are reassembled at the nip line of
the two friction rollers to form a yarn.
· As
soon as each fibre reaches the nip line, it is twisted on the forming strand by
the friction rollers.
· Slivers
are prepared for friction spinning in a similar way as those for rotor spinning
but finer slivers are used in the friction spinning machine.
· Up to 5
slivers are fed to the friction spinning machine.
· Feeding
channel is provided to convey the individualized fibres from an opening
cylinder into the nip of the yarn forming zone.
· The
fibres are twisted together into a yarn, alongside a suction slit in the yarn
forming zone generally formed by two friction rollers, in close proximity with each
other and driven in the same direction.
· The
process is assisted by air suction through the roller perforations.
· The resultant yarn is withdrawn from the nip
of the friction rollers and wound on a package.
·
Slivers are prepared for
friction spinning in a similar way as those for rotor spinning, except that
finer slivers are used. The fibre feeding device, the fibre transport device
and the twisting device are the three main operating stages of friction
spinning systems.
Main features of friction spinning:
The friction spinning system
with low spinning tension is suitable for the production of yarn at high speeds
up to 500 metres per minute.
This system produces
multicomponent yarns from a wide range of different fibres for technical
applications.
Limitations of friction spinning:
The friction spinning systems
have many limitations which restrict their acceptance as a viable system for
producing general-purpose yarns. The main limitations of the friction spinning
method are given below:
· The yarn
spun on the friction spinning machine poses lower tensile strength.
· The friction
spinning machine produces relatively weak yarn due to poor fibre orientation.
· The
extent of poor fibre orientation and buckling is greater with longer and finer
fibres in the friction spinning.
· Due to
quite high surface to core twist variation in the friction spinning, the
friction spun yarn shows low tensile strength.
· The
count range in the friction spinning method is limited. It is not possible to produce fine yarn.
· The yarns
spun on the friction spinning machine poses higher tendency of snarling.
· In the
friction spinning method, the unevenness and imperfections also increase due to
higher production speed.
Principle of operation of friction spinning
machine:
The friction-spinning system
is based on the principle of open-end spinning, which consists of the following
operations:
1- Sliver
feeding system
2- Fibres opening, drafting and individualization system
3- Fibres
reassembling and twist insertion system
4- Yarn winding system
Sliver feeding, drafting and individualization system:
· There are two methods of fibre feeding systems,
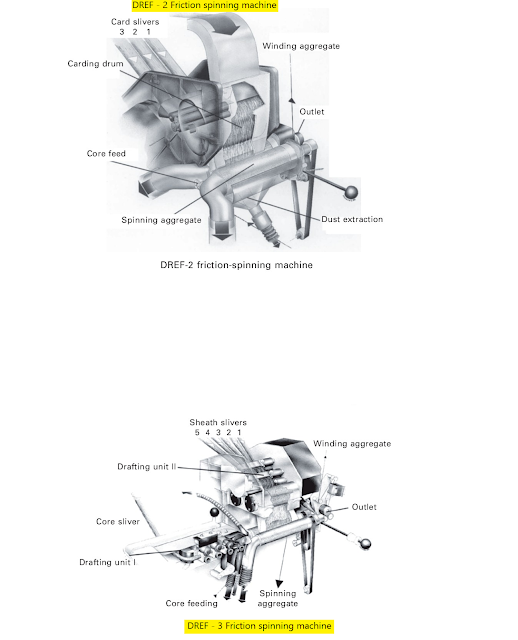
· Vertical feeding system is used in DREFII, DREF-III and DREF-2000 friction spinning machines.
· The inclined fibre feeding system is used in the PSL Masterspinner and DREF-5 spinning machine.
· Multiple slivers are fed vertically
· This
method has been found to be suitable only for production of coarser yarns.
· According
to studies feeding the fibre stream at an oblique angle onto the drum is the
best solution for production of finer yarns.
· Some studies have also suggested that inclined fibre feed offers advantages such as better fibre length utilization as well as spinning of finer yarns.
· The fibre feeding device also performs fibres individualization process.
· An opening roller, pinned beater or carding drum is used for fibre to fibre individualization.
· The fibre feeding device also performs fibre drafting process.
· The carding drum or opening rollers are covered with saw tooth wire clothing.
Fibre transport system:
· The fibre transport device feeds the individualized fibres into the yarn forming zone.
· The individualized fibres are transferred by air flow through the transport channel and deposited in the nip of the friction rollers.
·There are two modes of fibre feed, namely vertical feed and inclined fibre feed. DREF-2 and DREF-3 have vertical feed systems.
· The fibres are fed at right angles to the yarn axis.
·The Masterspinner employs an inclined fibre feed known as the backward-feed system
· The DREF-5 has an inclined fibre feed known as the forward-feed system.
Twist insertion system:
· The
twisting device consists of two friction rollers with surface motion in
opposite directions.
· The
motion of the friction rollers twists the fibre assembly and strengthens it.
· The
resulting ‘twist potential’ does not correspond to the ratio of yarn diameter
to friction roller diameter, as about 80–90% of it is lost through slipping.
· The
twist efficiency increases with increased air suction pressure.
· However,
the twist efficiency depends on many factors, including machine, process and
raw materials parameters.
· For a
stable spinning process, the frictional forces acting between the yarn surface
and the two rotating friction rollers should be, as far as possible, equal in
value.
· The
design and adjustment of friction rollers have a considerable influence on yarn
formation and ultimately on yarn.
Important design parameters of the
friction rollers influencing yarn formation:
The important design
parameters of the friction rollers that influence yarn formation are given
below:
1- The
shape, length and diameter of the friction rollers.
2- The
use of one or two perforated rollers each with suction at the spin-line.
3- The
hole size and percentage of perforations in the total roller surface.
4- The
finish of the friction roller surface.
5- The
adjustment of the suction cover plates.
6- The
stiffness and frictional properties of the rubber coating of the solid friction
roller when used with one perforated friction roller.
Important process parameters that
influence yarn formation and twisting efficiency:
The
important process parameters that influence yarn formation and twisting
efficiency are given below:
· The
air suction pressure
· The
dimensions and geometry of the nip between the friction rollers
· The
ratio of the friction roller surface speed to the yarn-take-off speed
· The
ratio of the rotating speeds of the two friction rollers
· The
direction of rotation when only one suction roller is used
· The
fibre-feeding device
· The
gap between the friction rollers
· The direction of yarn take-off
Yarn winding system:
The produced yarn is finally
wound on the yarn package. A cross wound yarn package results in the winding. A
suitable yarn winding attachment is fitted at the end of the machine to perform
the winding process.
You may also be interested in the below articles:
AIRJET/ VORTEX SPINNING METHOD (A OPEN END SPINNING PROCESS)
OPEN END YARN SPINNING METHOD ( ROTOR SPINNING PROCESS)










No comments:
Post a Comment