Loose reed motion ( warp protector motion):
Objective of loose reed motion:
When a shuttle loom works, there is always a chance to trape the shuttle in the shed. Since the reed performs beating motion, the shuttle gets beaten by the reed in case of shuttle trapped situation. the beating of the shuttle after trapping is a very serious problem during weaving. Multiple warp breakages get occurred in this situation. The shuttle and reed may be damaged. The loose reed motion mechanism prevents multiple warp breakages, damage to the reed and shuttle.
In this way, we can say that the main objective of the loose reed motion mechanism is to prevent the multiple breakages of warp and damage of shuttle and reed.
Structure of loose reed motion:
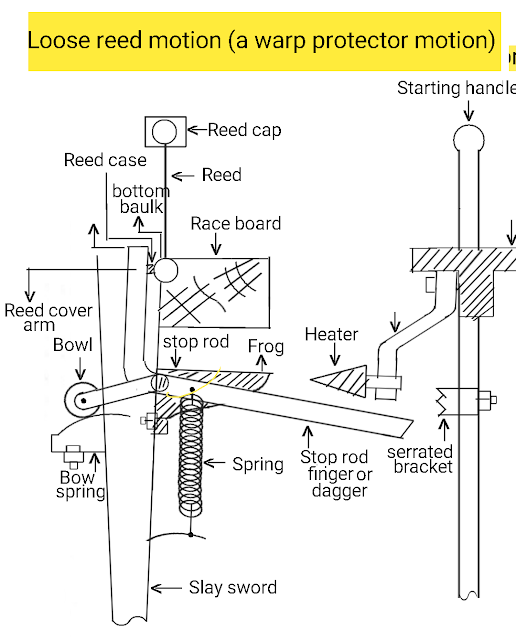
Reed is mounted in the reed case and reed cap. The reed cover arm helps to hold the reed firmly. This reed cover arm looks in L shape. It gets fulcrummed near the joint of the dagger or stop rod finger. An anti-friction bowl is also connected with a stop rod. The anti-friction bowl presses the bow spring in normal running condition. A spiral spring is also connected with the stop rod. A frog is attached to the stop rod. A heater is mounted on the starting handle in such a way that that frog passes under it in normal running conditions. A serrated bracket is mounted on the starting handle. The dagger does not push this serrated bracket in normal working.
Working principle of loose reed motion:
The reed is gripped in between the reed cap and reed case firmly by the reed cover arm. When the shuttle travels from one shuttle box to another shuttle box, it exerts pressure on the reed. The tension of the bow spring helps to keep the reed in the reed case firmly. This bow spring does generate the pressure equal to that pressure that gets applied to the reed during the beating. Therefore a spiral spring mounted on the stop rod helps to hold the reed firmly in case of beating motion.
In normal running conditions, the frog gets passed under the heater and the dagger does not push the serrated bracket.
When the shuttle gets failed to reach to opposite shuttle box, the shuttle either flys from the shed or gets trapped into the shed.
We know very well that reed beats every inserted pick after pick insertion. The reed beats the shuttle in case of shuttle trapping. This trapped shuttle beating causes multiple warp breakages and damage of shuttle and reed.
As the shuttle gets trapped in the shed, the loose reed motion mechanism comes into play immediately. The pressure getting applied on the reed during beating motion gets increased in case of shuttle trapping.
This increased beating pressure transfers to the reed cover arm. the bottom baulk of the reed comes out of the reed case. and reed does strike to the trapped shuttle hardly. the warp, red, and shuttle remain safe.
Since the reed cover arm gets fulcrummed at its fulcrum point, the reed cover arm receives a partial angular motion.
The reed cover arm is connected to the stop rod so that the stop rod lifts up. The frog comes over the heater. The heater increases the lift of the frog. The dagger mounted on the stop rod comes in front of the serrated bracket and pushes it. In this way, the starting handle gets disengaged and the loom gets stopped immediately.





No comments:
Post a Comment